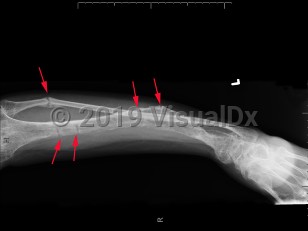
Familial hypophosphatemic rickets is a group of familial disorders characterized by hypophosphatemia and rickets as well as resistance to physiologic vitamin D repletion. The most common of these is X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets (XLH), in which an inactivating mutation leads to elevated serum fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) levels, resulting in renal phosphate wasting. Sometimes the condition can arise from a spontaneous mutation.
Some forms may be inherited in an autosomal dominant or recessive pattern. Familial hypophosphatemic rickets is sometimes associated with benign tumors that produce a humoral factor that decreases proximal renal tubular resorption of phosphate.
Clinical presentation is variable and typically presents after 18 months of age or when the pediatric patient begins to walk. Symptoms range from growth retardation and short stature to severe rickets or osteomalacia. Some patients have isolated hypophosphatemia detected on serologic testing. The typical presentation is a child with leg bowing and other bone deformities, pseudo-fractures, bone pain, and short stature. Rarely, a patient may present with tetany, dental enamel defects, and spine or pelvic rickets.
Treatment consists of oral phosphate supplementation and calcitriol. Adult patients with familial hypophosphatemic rickets of oncogene origin will usually improve once the tumor causing the disease is removed.
Familial hypophosphatemic rickets in Adult
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Codes
ICD10CM:
E83.31 – Familial hypophosphatemia
SNOMEDCT:
72831007 – Vitamin D-dependent rickets, type 2
E83.31 – Familial hypophosphatemia
SNOMEDCT:
72831007 – Vitamin D-dependent rickets, type 2
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:05/06/2019
Last Updated:07/06/2022
Last Updated:07/06/2022
Familial hypophosphatemic rickets in Adult