If suspicion is high, based on history of present illness (HPI), examination, and/or patient history:
- Assess vital signs.
- Establish reliable intravenous (IV) access.
- Blood pressure and heart rate control.
- Analgesia.
- CT angiogram of chest / abdomen / pelvis.
- Expedited consultation with vascular specialist.
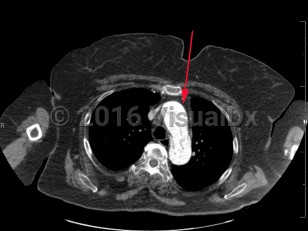
Aortic dissection is an intramural tear of the aorta. Aortic dissection is a life-threatening emergency. Tears often occur in the intimal layer of the aorta, with blood collecting in the medial layer. Back pain is the common presenting symptom, but it may also present with chest pain, dyspnea, or a new neurologic deficit. Syncope and hypotension occur less frequently. Aortic dissections most often occur in older men.
Aortic dissection can arise from several etiologies:
- Blunt trauma to chest / abdomen
- Chronic hypertension or hypertensive emergency
- Aortic atherosclerosis
- Sympathomimetic abuse / intoxication (eg, cocaine)
- Connective tissue disease (eg, Marfan syndrome)
- Acute increase in intrathoracic / intraabdominal pressure (eg, weight lifting, labor)
- Recent aortic instrumentation / procedure
- Aortic aneurysm dissection (less common)
- Type A – dissection involving ascending aorta
- Type B – dissection that does not involve ascending aorta (ie, aortic arch and descending aorta)
- DeBakey I – ascending and descending
- DeBakey II – ascending only
- DeBakey III – descending only
Related topic: cystic medial necrosis