Legionellosis
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Almost all cases of legionellosis are a result of inhalation of aerosolized bacteria contaminating warm man-made water bodies, such as water heaters, air conditioning equipment, cooling towers, warm-water baths, warm-water plumbing systems, and recirculating water systems. Contamination of such water systems in hospitals has led to nosocomial outbreaks of disease. Person-to-person transmission does not occur.
Legionellosis is believed to occur throughout the world. In the United States, about 9000 confirmed cases were reported each year in 2018 and 2019; the actual incidence is likely higher. The majority of patients were hospitalized for treatment. Most cases are sporadic. Less than one-fifth of all cases are associated with an outbreak, including health care-associated and travel accommodation-associated outbreaks.
Cigarette smoking, chronic heart and lung disease, male sex, diabetes mellitus, end-stage renal disease, cancer, and advanced age (older than 50 years) are some of the host factors that increase the risk for contracting legionellosis. Patients who are immunosuppressed are at a higher risk for infection with L pneumophila. Occupational exposures increase risk, such as hospital employment, work as a heating and air-conditioning technician, and building maintenance work. Social exposures include hot tub use.
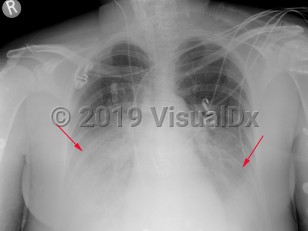
The incubation period is generally between 2-10 days, but cases with incubation periods as long as one month have been reported. A prodromal illness consisting of headaches, myalgias, weakness, diarrhea, and abdominal pain may occur. These symptoms may suggest a viral illness and lead to a misdiagnosis. Cough, shortness of breath, pleuritic chest pain, and fever (in some cases, 40°C [104°F] or higher) may develop. Mental confusion may be present. Clinical examination findings are nonspecific and may include focal rales or signs of lung consolidation. The viral-like prodrome that does not progress to pneumonia is also referred to as Pontiac fever and is self-limited. Pontiac fever has been recognized only during outbreaks of legionellosis.
Nonspecific findings such as pulse-temperature dissociation, hyponatremia, abnormal liver enzymes, lymphocytopenia, thrombocytopenia, disseminated intravascular coagulation, elevated creatine kinase (CK), and elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) have been described with legionellosis. These findings are insufficiently specific and sensitive to be of diagnostic value.
Rare cases of extrapulmonary disease have been described.
Codes
A48.1 – Legionnaires' disease
SNOMEDCT:
26726000 – Legionellosis
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:10/13/2024
 Patient Information for Legionellosis
Patient Information for Legionellosis - Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient