AIDS-associated Kaposi sarcoma - Oral Mucosal Lesion
See also in: Overview,External and Internal EyeAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

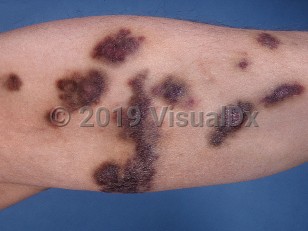
Kaposi sarcoma (KS) is a malignant neoplasm of lymphatic endothelial cell origin that occurs in several forms: AIDS-associated and non-AIDS-associated. Subtypes of non-AIDS-associated KS include classic KS, African endemic KS, and iatrogenic KS. All types of KS are due to or influenced by human herpesvirus type 8 (HHV-8), and cutaneous findings are clinically and histologically indistinguishable among the types. This summary focuses on the oral mucosal manifestations of AIDS-associated Kaposi sarcoma.
The outbreak of KS among young, previously healthy men who have sex with men (MSM) heralded the recognition of AIDS in 1981. AIDS-associated KS is the most common neoplasm in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-seropositive patients and is an AIDS-defining illness. This form of KS is primarily seen in the MSM population, but it can be seen in female partners of men with the disease in addition to HIV-infected women. Lesions may worsen during immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome and may also appear in patients with HIV who have received long-term antiretroviral therapy (ART).
Oral involvement may occur in about one-third of KS cases and may be the initial manifestation of KS in about 15% of cases. Oral involvement may at times precede cutaneous involvement. Oral lesions may be asymptomatic or may bleed, cause pain, or become secondarily infected. Oral lesions may be traumatized during regular chewing.
The introduction of ART dramatically decreased the incidence, morbidity, and mortality of AIDS-associated KS. ART should be considered first-line treatment for AIDS-associated KS.
The outbreak of KS among young, previously healthy men who have sex with men (MSM) heralded the recognition of AIDS in 1981. AIDS-associated KS is the most common neoplasm in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-seropositive patients and is an AIDS-defining illness. This form of KS is primarily seen in the MSM population, but it can be seen in female partners of men with the disease in addition to HIV-infected women. Lesions may worsen during immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome and may also appear in patients with HIV who have received long-term antiretroviral therapy (ART).
Oral involvement may occur in about one-third of KS cases and may be the initial manifestation of KS in about 15% of cases. Oral involvement may at times precede cutaneous involvement. Oral lesions may be asymptomatic or may bleed, cause pain, or become secondarily infected. Oral lesions may be traumatized during regular chewing.
The introduction of ART dramatically decreased the incidence, morbidity, and mortality of AIDS-associated KS. ART should be considered first-line treatment for AIDS-associated KS.
Codes
ICD10CM:
C46.9 – Kaposi's sarcoma, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
420524008 – Kaposi's sarcoma associated with AIDS
C46.9 – Kaposi's sarcoma, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
420524008 – Kaposi's sarcoma associated with AIDS
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:01/01/2024
Last Updated:02/08/2024
Last Updated:02/08/2024
AIDS-associated Kaposi sarcoma - Oral Mucosal Lesion
See also in: Overview,External and Internal Eye