Lymphomatoid granulomatosis
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

LyG is mainly prevalent in adults aged 45-65 years with a mean age of 48 years and a male-to-female ratio of 2:1, with rare pediatric cases. The most common presenting symptoms are fever, cough, malaise, weight loss, dyspnea, and chest pain. Less common symptoms include myalgias and arthralgias, symptoms produced by central nervous system involvement and peripheral neuropathy, as well as gastrointestinal (GI) complaints. Central and peripheral nervous systems are involved in approximately one-third of patients, with central nervous system involvement being a poor prognostic factor. Signs of brain involvement include confusion, ataxia, hemiparesis, and seizures. Cranial nerve involvement can cause Bell palsy, diplopia, amaurosis fugax, proptosis, sensorineural deafness, and central vertigo. Peripheral nervous system manifestations of LyG include distal (sensorimotor) polyneuropathy and mononeuritis multiplex LyG causes greater than 50% mortality, with most deaths occurring within 2 years of diagnosis. Cause of death is usually secondary to extensive destruction of the pulmonary parenchyma.
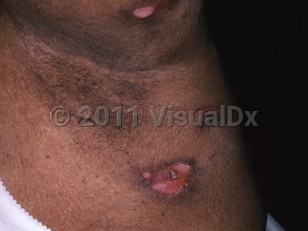
Skin involvement is seen in approximately 40% of patients. Lesions consist of dermal and subcutaneous nodules and ulcers (as a result of a lymphohistiocytic panniculitis). These may be painful but are classically asymptomatic. Uncommonly, macular erythema surrounding nodules or a more generalized eruption of macules and papules, which may be pruritic or asymptomatic, may be seen. The skin lesions can occur before, simultaneously, or after the lung lesions.
Risk factors include a prior history of lymphoma or leukemia, especially acute lymphocytic or myeloid leukemia in remission, inflammatory disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Crohn disease, ulcerative colitis, sarcoidosis, Sjögren syndrome, and various acquired and innate immunodeficiency states, including AIDS, posttransplantation states, variable immunodeficiency, X-linked agammaglobulinemia, hypogammaglobulinemia, DOCK8 deficiency, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, and impaired T-cell function.
Codes
C83.80 – Other non-follicular lymphoma, unspecified site
SNOMEDCT:
239940004 – Lymphomatoid granulomatosis
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:03/12/2024