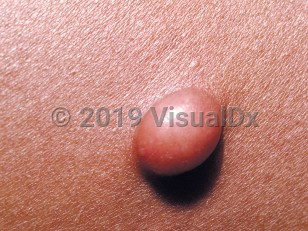
Solitary neurofibroma in Infant/Neonate
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Solitary neurofibromas are are well-circumscribed, non-encapsulated, benign tumors of neuromesenchymal tissue (Schwann cells, perineural cells, fibroblasts, and mast cells) with nerve axons. They present as asymptomatic, skin-colored or violaceous, rubbery papules or nodules. They can occur anywhere on the body. Solitary neurofibromas occur primarily in adulthood and late adolescence and are not an indication of neurofibromatosis. There is no sex predilection.
Codes
ICD10CM:
D21.9 – Benign neoplasm of connective and other soft tissue, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
404030000 – Solitary neurofibroma
D21.9 – Benign neoplasm of connective and other soft tissue, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
404030000 – Solitary neurofibroma
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:11/01/2018
 Patient Information for Solitary neurofibroma in Infant/Neonate
Patient Information for Solitary neurofibroma in Infant/Neonate
Premium Feature
VisualDx Patient Handouts
Available in the Elite package
- Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient
Upgrade Today