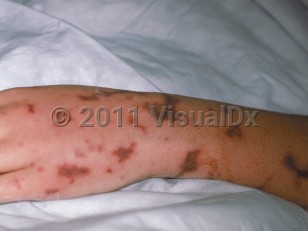
Purpura fulminans in Infant/Neonate
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

PF can be categorized into 3 types: acute infectious purpura fulminans, idiopathic or acquired purpura fulminans, and neonatal purpura fulminans. Acute infectious PF is the most common type and is associated with an acute infection and DIC. This type is due to an acquired deficiency of protein C secondary to the consumption of profibrinolytic cofactors. Decreased function of protein C induces a hypercoagulable state. The most common bacterial causes are Neisseria and Streptococcus pneumoniae, and varicella is the most common viral cause. PF develops in 10%-20% of patients with meningococcal septicemia. Urosepsis and staphylococcal sepsis are further common causes. Rickettsial disease, Capnocytophaga canimorsus (from a dog bite), and malaria may also lead to PF.
Acute illness, eg, septic shock, presents with high fever and rapid deterioration leading to hypotension and end-organ dysfunction. Physical or functional asplenia and immunosuppression increase the risk of developing acute infectious PF.
Idiopathic or acquired PF develops 7-10 days following a febrile illness, typically varicella or scarlet fever. It is rare and is due to an acquired protein S deficiency state. Anti-protein C or S antibodies bind to protein C or S. Cross-reacting immunoglobulin G (IgG) autoantibodies increase protein S clearance from the circulation and are thought to trigger postinfectious PF. Diminished protein S activity results in decreased activation of protein C and a subsequent hypercoagulable state. Acquired PF is associated with a lower mortality rate than the other types of PF.
Neonatal PF manifests early in life and is secondary to hereditary or acquired deficiency of protein C, protein S, or antithrombin III. See neonatal purpura fulminans for further discussion.
Codes
D65 – Disseminated intravascular coagulation [defibrination syndrome]
SNOMEDCT:
13507004 – Purpura fulminans
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:02/08/2023