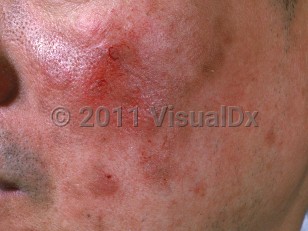
Pemphigus erythematosus
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

The age of onset and sex distribution are like that of pemphigus foliaceus (approximately age 50, occurs equally in men and women). As with other forms of pemphigus, pemphigus erythematosus is very rare in children.
Pemphigus erythematosus may persist almost indefinitely as a localized disease. Despite its name, most patients with pemphigus erythematosus do not develop signs of SLE. Patients with pemphigus erythematosus who also meet the American College of Rheumatology criteria for SLE are considered to have both conditions simultaneously.
Both clinically and immunopathologically, pemphigus erythematosus combines features of pemphigus and SLE. Patients have intercellular autoantibodies and subcorneal acantholysis as seen in pemphigus foliaceus. Patients also frequently have positive antinuclear antibodies (ANA) and a positive lupus band on direct immunofluorescence (DIF). In at least a subset of patients who are ANA-negative, the lupus band is thought to be be caused by deposition of circulating cleaved anti-desmoglein 1 antibodies along the basement membrane zone (BMZ), after ultraviolet radiation exposure.
Pemphigus erythematosus occurs with increased frequency in patients with a history of thymoma, myasthenia gravis, and other autoimmune diseases. Some of these patients also have autoantibodies directed against striated muscle. Certain HLA subtypes are represented more frequently in pemphigus erythematosus (HLA-A10, HLA-A26, HLA-DRW6).
Pemphigus erythematosus can be drug-induced. The most notable medications associated with this condition are d-penicillamine and captopril. Both agents contain a highly negatively charged sulfhydryl group that has been implicated as the potential cause of acantholysis. There are also reports of drug-induced pemphigus erythematosus with ceftazidime, propranolol, pyritinol, and heroin.
Pemphigus erythematosus has been reported to occur in lesions of ultraviolet burns and thermal burns. More rarely, pemphigus erythematosus has been reported to occur in the setting of malignancy, most commonly bronchogenic carcinoma.
In a 2003 article describing an outbreak of endemic pemphigus in Northern Columbia, pemphigus erythematosus was the primary clinical phenotype. On examination, most of the patients showed keratotic follicular skin lesions resembling discoid lupus erythematosus, a high degree of photosensitivity, and a lupus band-like deposition of immunoglobulins and complement at the BMZ.
Pemphigus erythematosus is less likely to rapidly progress than other forms of pemphigus and responds to similar immunosuppressant therapies.
Codes
L10.4 – Pemphigus erythematosus
SNOMEDCT:
36739006 – Pemphigus erythematosus
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:03/12/2024