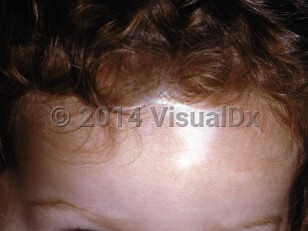
- WS type 1: Characteristically presents with dystopia canthorum (lateral displacement of the inner canthi) and frequently associated with poliosis (white forelock) and vitiligo on face or upper extremities. Complete or segmental heterochromia iridis and sensorineural hearing loss may also be seen. It is caused by a mutation of the PAX3 gene, and in most cases inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion.
- WS type 2: Characterized by the absence of dystopia canthorum and more frequently associated with heterochromia iridis and congenital sensorineural hearing loss. In most cases, it is due to a mutation of the MITF gene and is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion.
- WS type 3 (Klein-Waardenburg syndrome): Present with severe features of WS type 1 in association with upper limb abnormalities. It typically results from a mutation of the PAX3 gene that may be inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion. Severe cases may be related to the mutation homozygosity.
- WS type 4 (Waardenburg-Shah syndrome): Manifested by typical features of WS in association with Hirschsprung disease (aganglionic megacolon). It is caused by a homozygous mutation of the EDNRB or EDN3 gene or by a heterozygous mutation in the SOX10 gene.
Waardenburg syndrome in Infant/Neonate
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Waardenburg syndrome (WS) is a rare genodermatosis mainly characterized by variable degrees of facial dysmorphism, diminished pigmentation of skin, hair, or iris, and sensorineural hearing loss. Four different types of Waardenburg syndrome have been described, based on their distinct clinical findings and genetic mutations. Prominent features of each type include the following:
Codes
ICD10CM:
E70.89 – Other disorders of aromatic amino-acid metabolism
Q79.8 – Other congenital malformations of musculoskeletal system
SNOMEDCT:
47434006 – Waardenburg syndrome
E70.89 – Other disorders of aromatic amino-acid metabolism
Q79.8 – Other congenital malformations of musculoskeletal system
SNOMEDCT:
47434006 – Waardenburg syndrome
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:11/07/2017
Last Updated:01/25/2022
Last Updated:01/25/2022