Acinar cell carcinoma
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

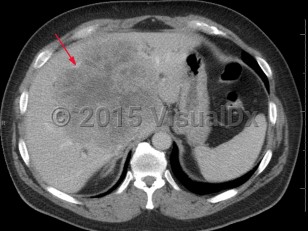
Acinar cell carcinoma is a rare malignant exocrine tumor of the pancreas resembling cells of the pancreatic acini. It comprises less than 1% of all pancreatic neoplasms and is usually a solid tumor. Its gross appearance is a pink to tan homogeneous growth. Tumors may grow to over 10 cm in diameter. Although seen most frequently in males of Northern European ancestry who are middle-aged or older, acinar cell carcinoma can occur at any age.
Findings include abdominal pain, a pancreatic mass, nausea, fatigue, weakness, elevated lipase, and weight loss. Some patients present with Schmid's triad (subcutaneous fat necrosis, polyarthritis, and eosinophilia) caused by elevated lipase secreted by the tumor.
Acinar cell carcinomas can easily be differentiated from adenocarcinoma and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors based on immunohistochemical stains. Overall prognosis depends on tumor size, lymph node involvement, and presence of metastasis at diagnosis.
Treatment includes surgical resection with potential chemotherapy or radiation.
Related topic: Pancreatic carcinoma
Findings include abdominal pain, a pancreatic mass, nausea, fatigue, weakness, elevated lipase, and weight loss. Some patients present with Schmid's triad (subcutaneous fat necrosis, polyarthritis, and eosinophilia) caused by elevated lipase secreted by the tumor.
Acinar cell carcinomas can easily be differentiated from adenocarcinoma and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors based on immunohistochemical stains. Overall prognosis depends on tumor size, lymph node involvement, and presence of metastasis at diagnosis.
Treatment includes surgical resection with potential chemotherapy or radiation.
Related topic: Pancreatic carcinoma
Codes
ICD10CM:
C80.1 – Malignant (primary) neoplasm, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
45410002 – Acinar cell carcinoma
C80.1 – Malignant (primary) neoplasm, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
45410002 – Acinar cell carcinoma
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:03/01/2018
Last Updated:03/01/2018
Last Updated:03/01/2018