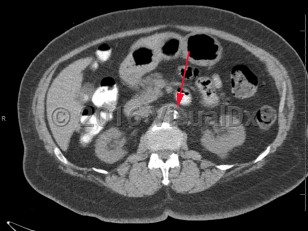
Renal artery stenosis
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Renal artery stenosis is narrowing or blockage of renal artery / arteries. Causes include atherosclerosis, fibromuscular dysplasia, thrombosis, embolism, or external pressure. Reduced renal perfusion can lead to renovascular hypertension as well as acute or chronic kidney injury.
Typically, affected patients will have a normal urinalysis. If both renal arteries are involved (as is more commonly seen with atheromatous disease), progressive renal impairment is observed, often with significant fluctuations in glomerular filtration rate dependent upon volume status.
Affected patients often have particular sensitivity to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor therapy, with (usually reversible) acute kidney injury evident on medication initiation. Severe hypertension with episodes of flash pulmonary edema may be seen with unilateral or bilateral disease.
Typically, affected patients will have a normal urinalysis. If both renal arteries are involved (as is more commonly seen with atheromatous disease), progressive renal impairment is observed, often with significant fluctuations in glomerular filtration rate dependent upon volume status.
Affected patients often have particular sensitivity to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor therapy, with (usually reversible) acute kidney injury evident on medication initiation. Severe hypertension with episodes of flash pulmonary edema may be seen with unilateral or bilateral disease.
Codes
ICD10CM:
I70.1 – Atherosclerosis of renal artery
SNOMEDCT:
302233006 – Renal artery stenosis
I70.1 – Atherosclerosis of renal artery
SNOMEDCT:
302233006 – Renal artery stenosis
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:05/12/2019