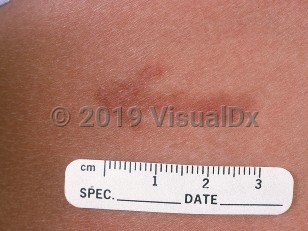
Caterpillar dermatitis in Child
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

The larvae of butterflies and moths, caterpillars are sometimes responsible for skin, eye, and systemic reactions in humans. Caterpillars do not sting like bees, hornets, or wasps, but they do cause irritation and allergic reactions in people by the "breakaway" spines or hairs that can inadvertently be implanted in the skin. Some caterpillars contain venoms located in their hairs and spines.
Most reactions range from mild dermatitis to erythemas and urticarial reactions, although contact with the South American saturniid moth or Lonomia caterpillars can cause consumptive coagulopathy, intracerebral hemorrhage, and acute renal failure. Lepidopterism refers to a systemic reaction to caterpillars and is characterized by a more widespread erythema or urticaria, nausea, vomiting, wheezing, conjunctivitis, and possibly headache. Caterpillar injuries have occurred worldwide and are more frequently reported in the Americas, China, Europe, and Australia.
Caterpillar hairs can also become airborne and cause outbreaks or small "epidemics" of dermatitis or urticaria simultaneous in many people. During the 1980s, the gypsy moth caterpillar caused outbreaks in New England. In addition to the skin findings, symptoms of caterpillar reactions include localized skin pain, pruritus, radiating pain toward the regional lymph nodes, paresthesias, and even muscle spasms. Most symptoms resolve within 24 hours.
Specific caterpillars and their geographic range include the following:
Saddleback caterpillar (Sibine stimulea)
Saddlebacks are one of the most common stinging caterpillars in the United States. Saddlebacks are relatively small, 2-3 cm in length, and have a prominent bright green midsection. These caterpillars are active in later summer and early fall throughout most of North America. Saddlebacks cause a painful "sting" associated with redness and edema.
Gypsy moth caterpillar (Lymantria dispar)
Gypsy moth caterpillars and other related tussock moth caterpillars are found in the United States, Europe, and Australia. These caterpillars can cause urticaria and dermatitis.
Browntail moth caterpillar (Euproctis chrysorrhoea)
Browntail moth caterpillars are found in the United States on the coast of Maine and Cape Cod, Massachusetts. Poisonous hairs cause a pruritic rash similar to that of poison ivy. The rash typically lasts a few hours to several days, although more severe cases can have a longer duration. If hairs are inhaled, respiratory distress may occur. In Australia, other Euproctis species that have been identified as causing rashes include the mistletoe browntail moth (Euproctis edwardsi), Euproctis baliolalis, Euproctis limbalis, and Euproctis lutea.
Io moth caterpillar (Automeris io)
The io moth caterpillar is found throughout the United States, southern Canada, and northern Mexico. The io moth caterpillar causes immediate pruritus and stinging of the involved skin. Reactions are transient and quickly resolve without systemic complications. The io moth caterpillar is 5-6 cm in length and pale yellow to green in color with red legs.
Buck moth caterpillar (Hemileuca maia)
The buck moth caterpillar has urticating spines and causes radiating pain similar to the saddleback caterpillar sting. There is localized edema and erythema. The buck moth caterpillar is 5-6 cm in length and has a brown to black body with white to yellow dots.
Lonomia South American moth caterpillar (Lonomia obliqua and Lonomia achelous)
Lonomia South American moth caterpillars can cause a life-threatening consumptive coagulopathy as described in the introduction to this synopsis. The caterpillars are found in Brazil, Venezuela, and Argentina and are 5-6 cm in length; they can be various colors but are usually brown or green.
Processionary tree caterpillar / Oak processionary moth (OPM) caterpillar
These are a family of caterpillars found worldwide. Processionary tree caterpillars have urticating hairs that cause outbreaks of dermatitis, allergic reactions, and rarely ophthalmia nodosa when hairs from the caterpillar penetrate the cornea.
Puss caterpillar (Megalopyge opercularis)
The puss caterpillar is the larval form of the flannel moth that inhabits the southeastern United States and Latin America. It is the most dangerous caterpillar in the United States. Its sting can cause excruciating local pain as well as systemic symptoms.
Most reactions range from mild dermatitis to erythemas and urticarial reactions, although contact with the South American saturniid moth or Lonomia caterpillars can cause consumptive coagulopathy, intracerebral hemorrhage, and acute renal failure. Lepidopterism refers to a systemic reaction to caterpillars and is characterized by a more widespread erythema or urticaria, nausea, vomiting, wheezing, conjunctivitis, and possibly headache. Caterpillar injuries have occurred worldwide and are more frequently reported in the Americas, China, Europe, and Australia.
Caterpillar hairs can also become airborne and cause outbreaks or small "epidemics" of dermatitis or urticaria simultaneous in many people. During the 1980s, the gypsy moth caterpillar caused outbreaks in New England. In addition to the skin findings, symptoms of caterpillar reactions include localized skin pain, pruritus, radiating pain toward the regional lymph nodes, paresthesias, and even muscle spasms. Most symptoms resolve within 24 hours.
Specific caterpillars and their geographic range include the following:
Saddleback caterpillar (Sibine stimulea)
Saddlebacks are one of the most common stinging caterpillars in the United States. Saddlebacks are relatively small, 2-3 cm in length, and have a prominent bright green midsection. These caterpillars are active in later summer and early fall throughout most of North America. Saddlebacks cause a painful "sting" associated with redness and edema.
Gypsy moth caterpillar (Lymantria dispar)
Gypsy moth caterpillars and other related tussock moth caterpillars are found in the United States, Europe, and Australia. These caterpillars can cause urticaria and dermatitis.
Browntail moth caterpillar (Euproctis chrysorrhoea)
Browntail moth caterpillars are found in the United States on the coast of Maine and Cape Cod, Massachusetts. Poisonous hairs cause a pruritic rash similar to that of poison ivy. The rash typically lasts a few hours to several days, although more severe cases can have a longer duration. If hairs are inhaled, respiratory distress may occur. In Australia, other Euproctis species that have been identified as causing rashes include the mistletoe browntail moth (Euproctis edwardsi), Euproctis baliolalis, Euproctis limbalis, and Euproctis lutea.
Io moth caterpillar (Automeris io)
The io moth caterpillar is found throughout the United States, southern Canada, and northern Mexico. The io moth caterpillar causes immediate pruritus and stinging of the involved skin. Reactions are transient and quickly resolve without systemic complications. The io moth caterpillar is 5-6 cm in length and pale yellow to green in color with red legs.
Buck moth caterpillar (Hemileuca maia)
The buck moth caterpillar has urticating spines and causes radiating pain similar to the saddleback caterpillar sting. There is localized edema and erythema. The buck moth caterpillar is 5-6 cm in length and has a brown to black body with white to yellow dots.
Lonomia South American moth caterpillar (Lonomia obliqua and Lonomia achelous)
Lonomia South American moth caterpillars can cause a life-threatening consumptive coagulopathy as described in the introduction to this synopsis. The caterpillars are found in Brazil, Venezuela, and Argentina and are 5-6 cm in length; they can be various colors but are usually brown or green.
Processionary tree caterpillar / Oak processionary moth (OPM) caterpillar
These are a family of caterpillars found worldwide. Processionary tree caterpillars have urticating hairs that cause outbreaks of dermatitis, allergic reactions, and rarely ophthalmia nodosa when hairs from the caterpillar penetrate the cornea.
Puss caterpillar (Megalopyge opercularis)
The puss caterpillar is the larval form of the flannel moth that inhabits the southeastern United States and Latin America. It is the most dangerous caterpillar in the United States. Its sting can cause excruciating local pain as well as systemic symptoms.
Codes
ICD10CM:
L24.89 – Irritant contact dermatitis due to other agents
SNOMEDCT:
403146001 – Caterpillar dermatitis
L24.89 – Irritant contact dermatitis due to other agents
SNOMEDCT:
403146001 – Caterpillar dermatitis
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:04/09/2024
 Patient Information for Caterpillar dermatitis in Child
Patient Information for Caterpillar dermatitis in Child
Premium Feature
VisualDx Patient Handouts
Available in the Elite package
- Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient
Upgrade Today