Lung cancer
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

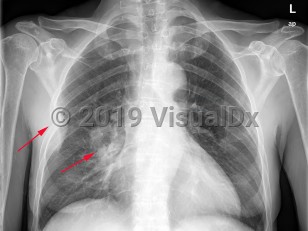
Greater than 95% of lung cancers can be categorized as either small cell lung cancer (SCLC) or non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), with adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma being the most common NSCLC. Carcinoid tumors and mesothelioma may also arise in the lung but are less common. The lungs are also a common site of metastatic cancer.
Some tumors may be associated with multiple metastases to the lung, which can cause rapid onset of pulmonary hypertension. Sometimes, cancer may invade the esophagus and cause a bronchoesophageal fistula. Lung cancer is a common cause of obstruction of the superior vena cava and superior vena cava syndrome. Cushing syndrome is a common paraneoplastic association.
Environmental and lifestyle factors have been associated with the development of lung cancer. These include cigarette smoking, environmental toxins, and radiation therapy. Lung cancer screening may be advisable in select patients. See nicotine dependence for information on smoking cessation.
The prognosis and treatment of lung cancer is dependent on the type of cancer present, lymph node involvement, and the presence or absence of metastasis. Treatment options include surgical resection, chemotherapy, and/or radiation.
Codes
C34.90 – Malignant neoplasm of unspecified part of unspecified bronchus or lung
SNOMEDCT:
363358000 – Malignant tumor of lung
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:01/25/2023